
How to Set-up Cloudwatch Agent and push Server/Application Logs to AWS Cloudwatch
Table of Contents
- AWS Cloud Watch Agent Use Cases
- Application Logs To AWS Cloudwatch Workflow
- Create an IAM role for Cloudwatch Agent
- Add the Cloudwatch Role to the Instance
- Install Cloudwatch Logs Agent
- Configure Cloudwatch Agent
- Conclusion
This article walks you through the steps involved in configuring the Cloudwatch agent on an ec2 instance and configure it to push the logs generated by the applications & system services.
Here is what you are going to learn in this blog.
AWS Cloud Watch Agent Use Cases
AWS Cloudwatch logs service has the capability to store custom logs and process metrics generated from your application instances. Here are some example use cases for custom logs and metrics
- Web server (Nginx, Apache etc ) access or error logs can be pushed to Cloudwatch logs it acts as central log management for your applications running on AWS
- Custom application logs (php, java, python, etc) can be pushed to cloudwatch, and you can set up custom dashboard's and alerts based on log patterns.
- Ec2 instance metrics/custom system metrics/ app metrics can be pushed to cloudwatch.
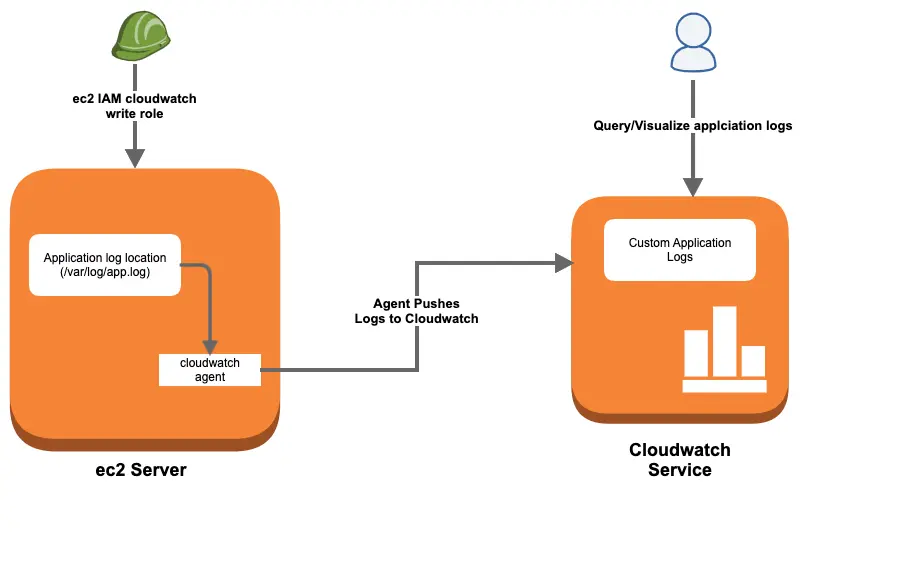
Application Logs To AWS Cloudwatch Workflow
You can send logs from any number of ec2 sources to Cloudwatch. All you need to have is a Cloudwatch agent running on your instance.
Here is what you have to do
- Create a custom ec2 IAM role with Cloudwatch log write access
- Install Cloudwatch logs ec2 agent
- Configure log sources in the Cloudwatch agent configuration file.
- Start the agent with the configuration file.
- Validate logs in Cloudwatch dashboard.
Note: In an actual project implementation the cloudwatch ec2 agent and configuration would be part of the AMI (Golden Image) or AMI packaging tool like packer.
Let’s get started with the setup.
Create an IAM role for Cloudwatch Agent
To set up AWS custom logs, first, you need to create and add a custom ec2 IAM role to your instance. This IAM role will have policies with write access to the Cloudwatch service so that all the logs from ec2 instances can be shipped to Cloudwatch.
Before creating a role, you need to create a custom policy.
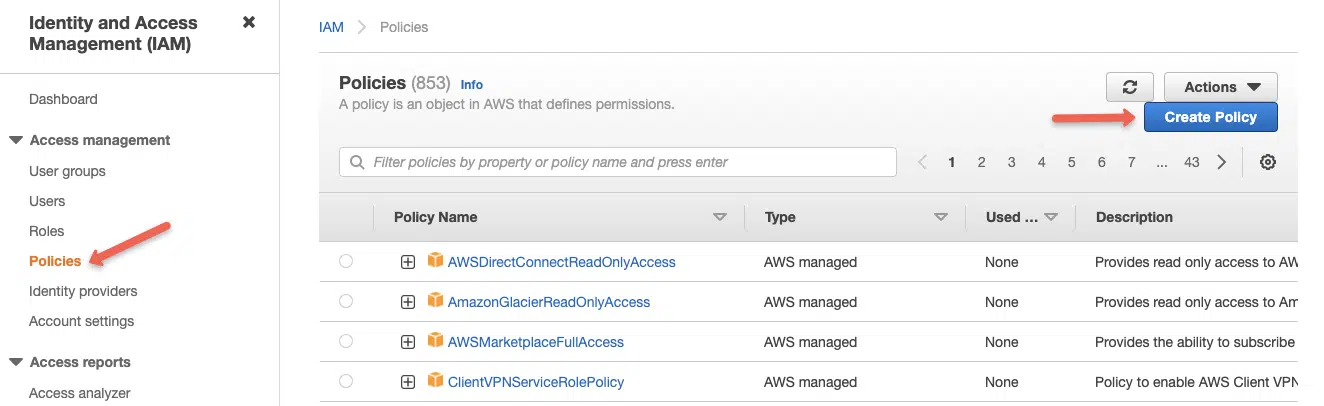
Step 1: Head over to AWS IAM –> Policies –> Create Policy
Step 2: Select the JSON option
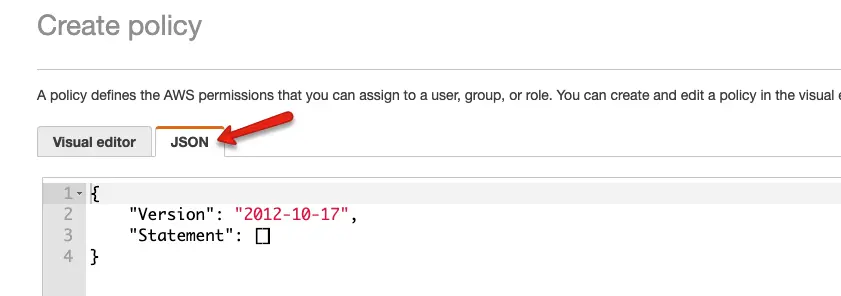
Step 3: Copy the following content in the policy block. We are allowing the required permissions, and the logs arn details.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": \[
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": \[
"logs:CreateLogGroup",
"logs:CreateLogStream",
"logs:PutLogEvents",
"logs:DescribeLogStreams"
\],
"Resource": \[
"arn:aws:logs:\*:\*:\*"
\]
}
\]
}
On the next page, add a tag to the policy. give a name, description for your policy, and click Next
On the next page, add a policy name, description and click create policy.
create IAM policy for pushing cloudwatch logs
Once you create the policy, you need to create a role with the custom policy you have created.
Step 4: Head over to AWS IAM –> Roles –> Create Role and select options as shown below.
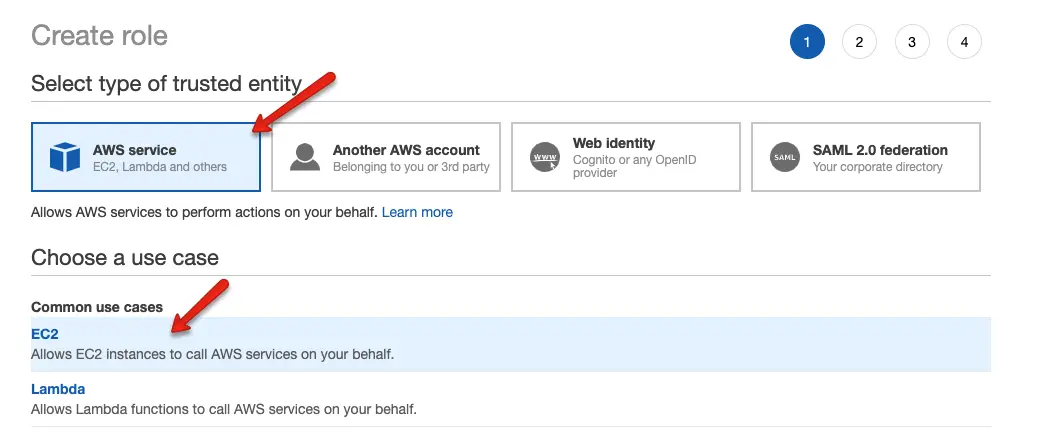
Step 5: From the filter, select “Customer Managed” and select the Policy you created in step 3.

Step 6: Next, enter a role name and create the role.
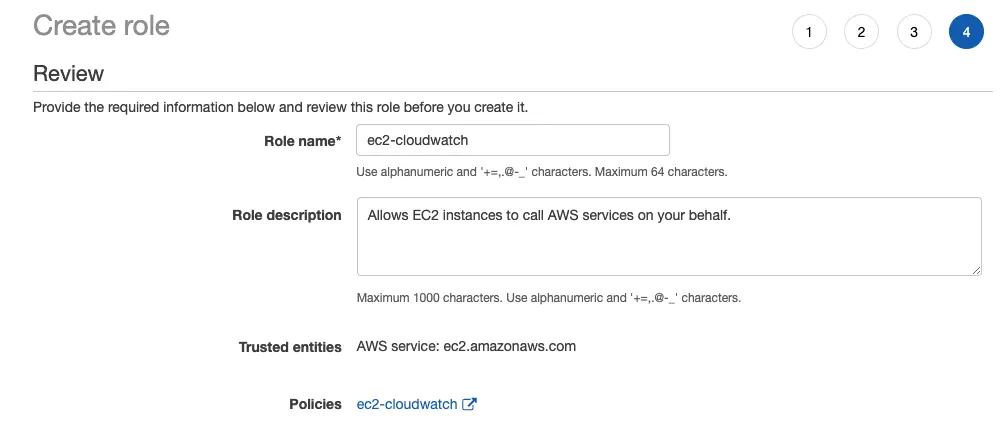
Add the Cloudwatch Role to the Instance
Follow the steps given below to add the custom IAM role to the ec2 instance where you want to set up the cloud watch agent.
- Head over to ec2 and select the instance in which you want to configure the custom logs.
- Right-click for options and select
Securityand then chooseModify IAM Roleoption. - Select the custom cloud watch IAM role from the dropdown and save it.
Install Cloudwatch Logs Agent
SSH into the ec2 instance and follow the steps given below.
Step 1: Head over to the Cloudwatch agent downloads page. You can select regions wise package as well.
Step 2: Download the appropriate agent installation file.
In my case it’s ubuntu. I am downloading the latest Ubuntu package and installing it.
wget https://s3.amazonaws.com/amazoncloudwatch-agent/ubuntu/amd64/latest/amazon-cloudwatch-agent.deb
sudo dpkg -i amazon-cloudwatch-agent.deb
Redhat users,
wget https://s3.amazonaws.com/amazoncloudwatch-agent/redhat/amd64/latest/amazon-cloudwatch-agent.rpm
rpm -U amazon-cloudwatch-agent.rpm
Configure Cloudwatch Agent
After the installation, you can find all the cloudwatch agent-related config files and executables in the following location.
/opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent
Here is the tree structure of the files present in the directory.
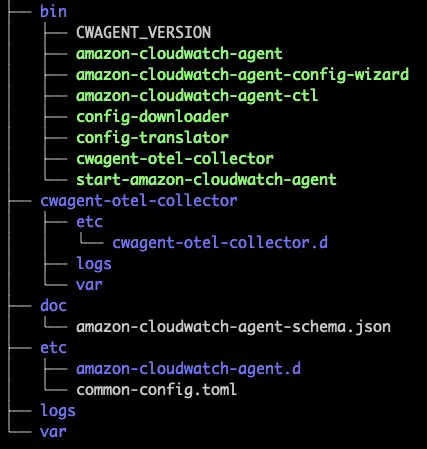 ](/images/blog/push-serverapplication-logs-to-aws-cloudwatch/image-19.png.webp)
](/images/blog/push-serverapplication-logs-to-aws-cloudwatch/image-19.png.webp)
If you are just starting with a cloud watch agent, it is better to run the cloud watch agent wizard that helps you create the log agent configurations. It prompts you with all the agent-related questions.
For the question, Do you want to store the config in the SSM parameter store?, select No.
The final config files get stored in the following location/
/opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/bin/config.json
In my case, I am going to replace the default config.json with a custom config.json that collects the following logs.
- Cloudwatch agent logs
- System logs from
/var/log/messages - Nginx access logs from
/var/log/nginx/access.log - Nginx error logs from
/var/log/nginx/error.log
Note: Install Nginx, if you want to follow the following configs for testing purposes. Or you can use you can replace the log locations with your applcation log path.
Here is the final cloudwatch agent config.
{
"agent": {
"metrics_collection_interval": 10,
"logfile": "/opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/logs/amazon-cloudwatch-agent.log",
"run_as_user": "root"
},
"logs": {
"logs_collected": {
"files": {
"collect_list": [
{
"file_path": "/opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/logs/amazon-cloudwatch-agent.log",
"log_group_name": "/apps/CloudWatchAgentLog/",
"log_stream_name": "{ip_address}_{instance_id}",
"timezone": "Local"
},
{
"file_path": "/var/log/messages",
"log_group_name": "/apps/system/messages",
"log_stream_name": "{ip_address}_{instance_id}",
"timestamp_format": "%b %d %H:%M:%S",
"timezone": "Local"
},
{
"file_path": "/var/log/nginx/access.log",
"log_group_name": "/apps/webservers/nginx/access",
"log_stream_name": "{ip_address}_{instance_id}",
"timestamp_format": "%d/%b/%Y:%H:%M:%S %z",
"timezone": "Local"
}
]
}
}
}
}
Now, let’s start the Cloudwatch agent using the following.
sudo /opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/bin/amazon-cloudwatch-agent-ctl -a fetch-config -m ec2 -c file:/opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/bin/config.json -s
You can check the agent status using the following command.
sudo /opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/bin/amazon-cloudwatch-agent-ctl -a status
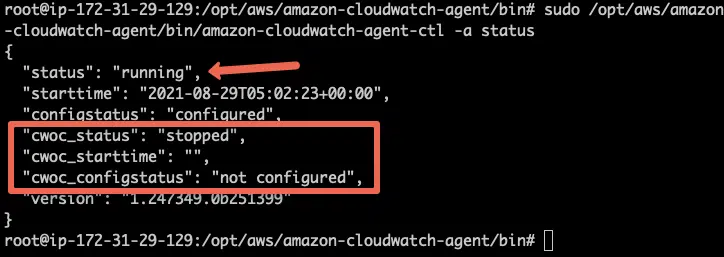
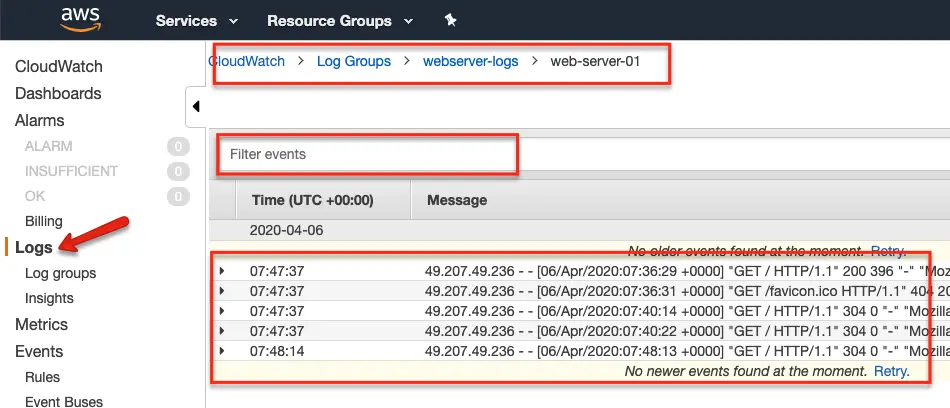
Validating Custom Logs in Cloudwatch Dashboard
Once the setup is done, you can view all the configured logs under the cloudwatch dashboard (under the logs option)
- Go to Logs –> Log Groups and you will see the log group you mentioned in the agent configuration.
- Select the log group and you should see your instance identified you mentioned in the config.
- If you click the instance identifier, it shows all the logs. You can use the cloud watch filter option to filter and query required logs.
Conclusion
I have explained the Cloudwatch logs agent setup to push application logs to the Cloudwatch logging service. It is a manual setup.
If you want this to be automated, all the agent configuration has to be baked in the ec2 AMI. Few configurations can be added at the system startup using the user data scripts. Again, it depends on what workflow you are opting for.
Not only just logs, but you can also push custom metrics to cloudwatch for monitoring.
If you face any issues or have any different ideas, do let me know in the comment section.
Comments (0)
What are your thoughts on "How to Set-up Cloudwatch Agent and push Server/Application Logs to AWS Cloudwatch"?
You need to create an account to comment on this post.
Related articles










